Introduction:
In the fast-moving hospitality business of today, never has it been more critical to choose the best point-of-sale (POS) system for your restaurant. For a small bistro, food truck, or full-service restaurant, the appropriate restaurant POS system can help to streamline your operations, make your customers happy, and boost your overall profits.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!However, out of all the choices available, it’s important to thoroughly understand the various POS systems to choose the right POS for your restaurant and also make the perfect investment. From traditional terminal POS systems to cloud-based POS systems, there is always some option available for every restaurant concept in the market.
Each POS system has distinct characteristics, pricing model, and amount of flexibility. POS systems share some features specifically designed for full-service restaurants (FSRs) such as table management, tipping, and extended reporting, while others are for quick-service restaurants (QSRs) with high-volume transactions.
The most widely used types of POS systems in restaurants are mobile POS, cloud based POS systems, self-service kiosk POS ,tablet POS systems, quick service POS, iPad restaurant POS and hybrid models through this article.
Fast food POS systems provide speedy order processing, live inventory tracking, quicker checkouts, sales reports, and less error. They support customer service, automate, and support loyalty programs and promotions.
When searching for the best POS systems for restaurants, it typically involves a combination of hardware, software, and integrations dedicated to the requirements of different types of restaurants (i.e., quick-service restaurants, full-service restaurants, cafes, and food trucks).
By this blog we are highlighting how every system integrates aspects such as inventory management, staff scheduling, online order integration, and payment processing—easing the process of choosing the optimal restaurant POS system for your business in 2025 and beyond.
Also Read: Best Marketing Strategies for Restaurants
What Is a Restaurant POS System?
A restaurant POS system comprises a combination of software and hardware intended to oversee sales transactions, order management, and overall restaurant operations.
Livelytics emphasizes that a restaurant POS system is the foundation of restaurant operations, providing smooth communication of front of house (FOH) and back of house (BOH) operations.
Modern POS systems commonly offer integrations for accounting, inventory, scheduling employees, online ordering, and more.
Also Read: Why are so Many Restaurants Closing
POS Features for Restaurants:
Here is a clear and organized list of POS features designed specifically for restaurants:
1. Order & Table Management:
- Handheld device table-side ordering
- Floor plan and table layouts that can be customized
- Bill splitting and split checks
- Course-by-course ordering
- Real-time table status (open, seated, billed)
Also Read: How AI is improving the Table Turnover Rate in Restaurants
2. Menu Management:
- Simple menu modifications and item updates
- Creation of daily specials and combo meals
- Syncing of menus across multiple locations
- Modifier options (e.g., extra cheese, no onions)
Also Read: Food Menu Ideas for Restaurants
3.Inventory Management:
- Real-time stock levels
- Ingredient-level monitoring
- Low-stock and expiry warnings
- Automatic inventory deduction per sale
Also Read: AI for Retail Inventory Management
4.Kitchen Integration
- KDS compatibility
- Digital order routing to the kitchen/bar
- Order prioritization and prep status tracking
- Less errors vs handwritten tickets
Also Read: Key Metrics Restaurant Owner Should be Tracking
5. Payment Processing
- Supports cash, credit/debit, mobile wallets, gift cards
- Supports contactless payments and QR code payments
- Tip and gratuity handling
- Split payments and partial payments handling
Also Read: How Restaurant Can Predict Trends With Analytics
6.Staff & Employee Management
- Clock-in/clock-out and time tracking
- Tracks employee sales performance
- Role-based permissions and access
- Payroll integration
Also Read: How Can Data Analytics Improve the Measurement of Employee Performance
7.Reporting & Analytics
- Sales, labor, and inventory reports
- Daily/weekly/monthly revenue tracking
- Peak hours and best-selling items analysis
- Exporting data and dashboard customization
Also Read: Business Intelligence and Data Analytics Services
8.Customer Management & Loyalty
- Manages customer profiles and visit history
- Integrated loyalty programs and points tracking
- SMS/email marketing integrations
- Feedback collection and survey instruments
Also Read: The Importance of Customer Analytics in Retail
9.Integration with Online Ordering & Delivery
- Online ordering directly from your site
- Uber Eats, DoorDash, Grubhub, and others integration
- Sync between online and in-store orders in real-time
- Delivery dispatch and tracking features
Also Read: How AI Unlocks Business Insights that Drive Required Results
10.Mobility & Cloud Access
- Cloud access from any device
- Automatic software updates and data backups
- Offline mode to continue running during outages
Also Read: How to Open a Convenience Store
11.Security & Compliance
- PCI DSS compliance
- Transaction encryption and data protection
- Staff login by PIN or biometrics
- Activity logs and fraud prevention
Also Read: What is the Main Reason of Using Data Analytics in Revenue Analysis
Traditional vs. Modern POS Systems : Key Differences
1.Hardware:
Traditional POS uses heavy, fixed terminals; modern POS runs on tablets or mobile devices.
Also Read: Livelytics Named Semi-Finalist in Startup Alley
2.Software Updates:
Traditional POS needs updates done manually; modern systems automatically update through the cloud.
Also Read: What is Business Intelligence and Why Does it Matter
3.Data Storage:
Traditional POS systems store data in local servers; modern POS relies on cloud storage for remote access.
Also Read: Two Way Data Analytics in Shaping Retail Business
4.Mobility:
Traditional POS is fixed; modern POS is mobile and operates tableside or off-site.
5.Cost:
Traditional systems are expensive to set up; modern POS is less expensive to set up with monthly charges.
Also Read: Retail Pricing Strategy
6.Flexibility:
Modern POS has more integrations and scalability, which suits changing restaurant needs.
Also Read: Improved Decision Through Decision Intelligence
Cloud POS vs. On-Premise POS: Key differences.
1. Installation & Setup:
- Cloud POS: Rapid setup; operates on online-connected devices.
- On-Premise POS: Needs in-premise server deployment and hardware.
Also Read: How Business Intelligence is Helping Businesses
2. Accessibility:
- Cloud POS: Retrieve data anywhere using the internet.
- On-Premise POS: Restricted to location alone.
Also Read: What is the Main Reason for Using Data Analytics in Revenue Analysis
3. Updates & Maintenance:
Cloud POS: Providers handle automatic updates.
On-Premise POS: handles manual upgrades; requires IT support.
Also Read: Key Metrics Every Restaurant Owner Should Be Tracking
4. Cost Structure:
Cloud POS: has subscriptions, minimal upfront costs.
On-Premise POS: High initial expense, less repeated fees.
Also Read: How to Calculate Food Cost Percentage
5. Scalability:
Cloud POS: Scalable as needed for expansions or multiple branches.
On-Premise POS: Scaling needs more hardware and configuration.
Also Read: How to Increase Restaurant Sales Without Advertising
6. Offline Capability:
Cloud POS: Offline use is restricted except in hybrid mode.
On-Premise POS: Works fully without the internet.
How Restaurant POS works?
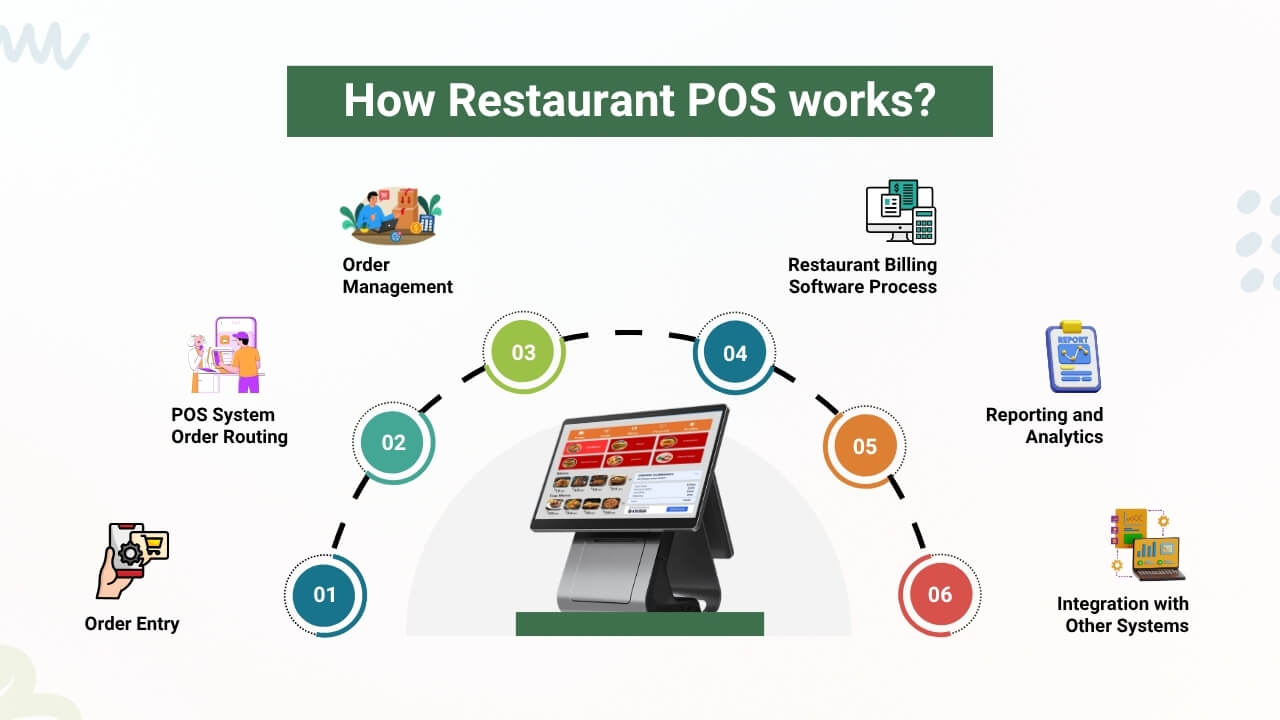
A restaurant point-of-sale (POS) system is the central hub for order processing, payment management, and front- and back-of-house coordination. Modern POS systems don’t just process transactions; they manage the whole process from when an order is received to when the payment is made.
1. Order Entry:
The process starts when a server or cashier enters a customer’s order into the POS system through a touchscreen kiosk, tablet, or handheld. In quick-service restaurants, this may happen at a counter; in full-service restaurants, it may happen tableside.
A restaurant POS Order Management System controls order entry, routing, tracking, payment processing, and fulfillment for dine-in, takeout, and online ordering.
Also Read: AI for Restaurant Marketing
2. POS System Order Routing:
Once the order is put in, the POS posts it directly to the kitchen display system (KDS) or it prints out a ticket on a kitchen printer. This reduces error and communication delay between waiters and kitchen staff.
Also Read: How Does Data Analytics Help Restaurant Grow
3. Order Management:
Order Management for restaurant POS systems simplifies order entry, routing to kitchen, progress tracking, and fulfillment management, guaranteeing efficient service, minimizing errors, and smooth coordination between front and back of house. The POS system keeps a record of active orders, table status, and modifiers (“extra cheese” or “no onions”).
Also Read: Mobile Marketing for Restaurants
4. Restaurant Billing Software Process:
Restaurant billing software manages order calculations, tax and discount calculations, bill splitting, tip handling, and payment handling. It provides proper billing, integrates with POS systems, and provides electronic or printed receipts to customers.
Also Read: How Livelytics Can Help Restaurants Boost Revenue
5. Reporting and Analytics:
Reporting and Analytics in restaurant POS systems give restaurant owners real-time insights into sales, inventory, staff performance, and customer activity. Through such features, restaurant owners can make informed decisions, optimize business, cut costs, and increase profitability.
Also Read: How Restaurants Can Predict Trends With Analytics
6. Integration with Other Systems:
Integration with Other Platforms such as inventory management, online ordering, accounting software, payment gateways, Customer Relationship Management(CRM), and loyalty programs within POS streamlines operations, provides a better customer experience, and improves overall business efficiency.
It allows real-time data sharing between platforms, releasing it from manual work and improving accuracy. This creates a fully connected system that reduces manual intervention and improves accuracy in all operations.
Also Read: Benefits of Data-Driven Decision
Types of Restaurant POS Systems:
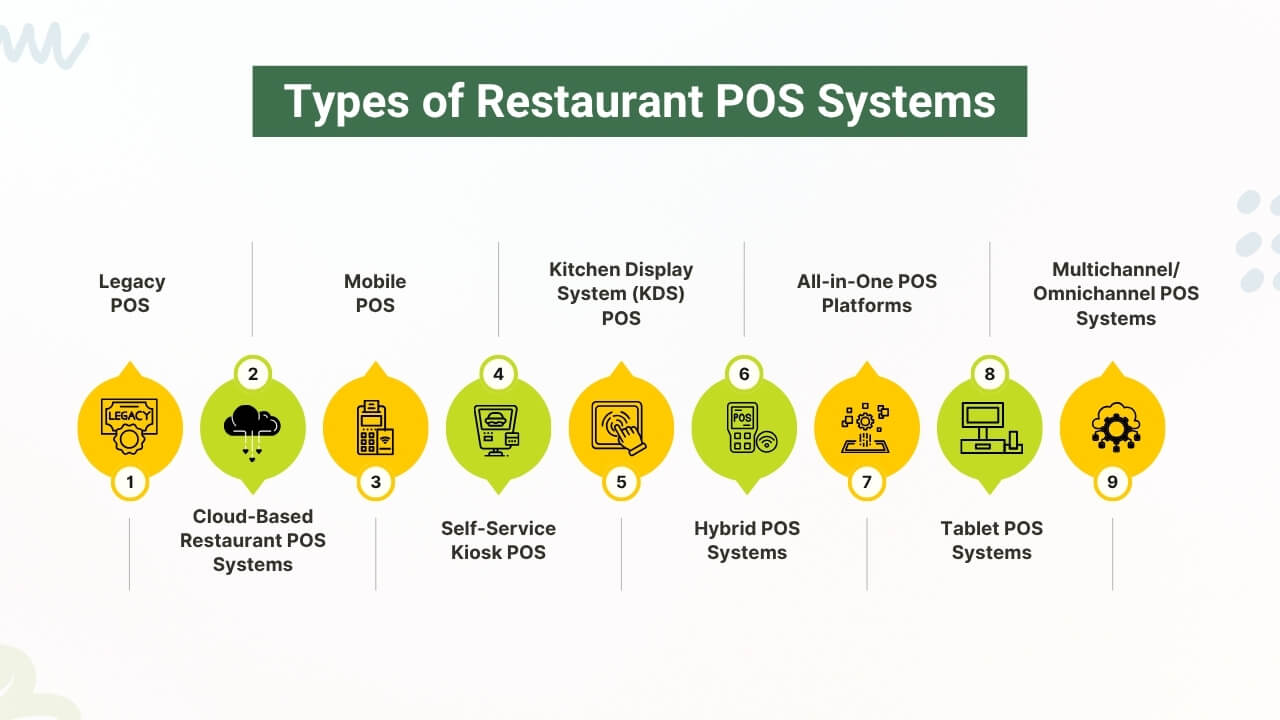
1. Legacy POS (Traditional POS Systems):
Legacy POS systems/Traditional POS systems are on-premises software solutions installed on local servers and hardware. They have fixed terminals and cash drawers that typically reside in larger or older restaurants. One well-known example of a Traditional POS System is Oracle MICROS POS.
MICROS POS is recognized for its strong, hardware-intensive configuration, offline reliability, and enterprise-level customizability. It’s best suited for big operations that require stability and advanced backend functionality without relying on the internet.
How It Works:
The data and software are kept on a local server in the restaurant. All reporting and transactions are done in-house, and the system typically needs physical networking and IT support.
Benefits:
1.Runs without internet
2.Secure and stable if properly maintained
3.Customizable hardware configuration
Drawbacks:
1.High initial cost for licensing and hardware
2.Needs manual updates and on-site IT assistance
3.No remote access to information
Best For:
Full-service restaurants, hotel restaurants, and large venues with complicated infrastructure and in-house IT capabilities.
Also Read: Business Intelligence for Restaurants
2. Cloud-Based Restaurant POS Systems:
Cloud Point of Sale systems for restaurants operate on internet-connected devices, with all data saved in the cloud. This allows remote access, automatic updates, and seamless scalability. A prime example of such a system is Toast POS, which is tailor-made for the restaurant sector.
Toast offers end-to-end management options that combine back office and front of house tasks, all being available on any device. Its cloud-based architecture facilitates real-time reporting and remote management, making it a flexible and scalable solution for growing businesses.
How It Works:
The system works by enabling employees to accept orders and process payments through tablets, computers, or smartphones, with data being synchronized in real time to a secure cloud server, providing access from anywhere.
Benefits:
1.Access real-time reports anywhere
2.Automatic updating and backups
3.Seamless scalability across many locations
Drawbacks:
1.Needs reliable internet connection
2.May include monthly subscription fees
Best For:
Small to midsize restaurants, cafes, fast-casual chains, and companies that require flexibility and scalability.
Also Read: Business Intelligence for Small Restaurants
3. Mobile POS (mPOS):
A Mobile POS for restaurants is a light, tablet- or smartphone-based solution that takes orders and makes payments on the move. A leading example of an Mobile POS system is Square POS.
Square POS is admired for its ease of use, affordability, and quick installation—perfect for small or mobile food establishments. You can accept orders and make payments anywhere, with or without Wi-Fi (offline mode included). It also links to other Square services such as online ordering and payroll.
How It Works:
Through apps on mobile devices, servers can take orders at the table, process payments at the curb, or manage transactions at pop-up venues.
Benefits:
1.Increases speed of service and mobility
2.Lower hardware cost
3.Perfect for line-busting or tableside ordering
Drawbacks:
1.Limited functionality if not part of a larger system
2.Could be internet or Bluetooth dependent
Best For:
Food trucks, pop-ups, restaurants, and cafes wanting to provide contactless or tableside service.
Also Read: Mobile Marketing for Restaurants
4. Self-Service Kiosk POS:
Self-service kiosk POS systems are touchscreen customer-facing terminals where guests can navigate the menu, order, and pay without staff intervention. One of the top Self-Service Kiosk POS examples is Toast Kiosk.
Toast Kiosk increases productivity and saves labor by enabling guests to order on their own—freeing up employees for food preparation and service. It’s completely integrated with Toast’s larger POS system, offering unified reporting, menu management, and customer insights.
How It Works:
Kiosks are installed in-store (usually in QSRs), with customers directly engaging with the system. Orders are sent directly to the kitchen, and payments are made on the spot.
Benefits:
1.Accelerates service and lowers labor costs
2.Decreases order mistakes
3.Promotes upsells through visual menus
Drawbacks:
1.Initial hardware capital expense
2.Not suitable for every customer base
3.Needs frequent cleaning and maintenance
Best For:
Quick-service chains, busy fast-casual restaurants, and airport or mall food courts.
Also Read: Self-Service Data Platform
5. Kitchen Display System (KDS) POS:
A KDS-integrated POS system links front-of-house activity to the kitchen through digital screens, removing paper tickets. One of the best examples of a Kitchen Display System (KDS) POS is Toast KDS.
Toast KDS eliminates paper clutter, streamlines kitchen operations, and reduces errors. It’s perfect for restaurants that want to automate the back of house with real-time communication between the FOH and BOH staff.
How It Works:
Digital orders go directly from servers or kiosks to kitchen screens. The system is updated live and assists in kitchen staff prioritization and monitoring of preparation times.
Benefits:
1.Enhances kitchen speed and accuracy
2.Monitors food prep statistics and order timing
3.Environmentally friendly (paperless)
Drawbacks:
1.Does require initial training and stable screens
2.Higher hardware expense than printers
Best For:
High-volume restaurants, busy kitchens, ghost kitchens, and multi-prep station operations.
Also Read: Food Menu Ideas for Restaurants
6. Hybrid POS Systems:
Hybrid POS systems blend the dependability of traditional POS with the adaptability of cloud-based systems. They are able to function offline and sync with the cloud when connected. One of the best Hybrid POS System examples is Revel Systems POS.
Revel’s hybrid design guarantees your restaurant keeps running seamlessly—even without an internet connection. It’s perfect for companies seeking the reliability of on-premise systems combined with the agility and remote access of cloud-based systems.
How It Works:
Data and transactions are stored locally when offline and uploaded to the cloud automatically once internet connectivity resumes. Such systems tend to contain both fixed and mobile equipment.
Benefits:
1.Offline capability
2.Real-time analytics and remote access
Drawbacks:
1.Greater setup and subscription fees
2.More complicated to keep up
Ideal For:
Restaurant chains, franchises, or businesses in regions where the internet is poor but there’s a requirement for cloud reporting and remote access.
Also Read: Domo Vs Power BI
7. All-in-One POS Platforms:
All-in-one POS systems for restaurants with modules such as inventory management, CRM, online ordering, loyalty schemes, and reporting functionality. A strong example of an All-in-One POS Platform is Lightspeed Restaurant POS.
Lightspeed combines everything a modern restaurant needs—whether you’re running a single location or a growing chain—into one intuitive and scalable system. It’s ideal for operators who want to eliminate multiple third-party tools and manage their entire business from a unified platform.
How It Works:
Everything is on one dashboard. Orders, customer information, payments, and stock are monitored and controlled in real time.
Benefits:
1.Smooth integration of several functions
2.Streamlined operations
3.One vendor and support point
Drawbacks:
1.Possibly excessive for very small enterprises
2.May be expensive depending on features included
Best For:
Growing restaurants, franchise businesses, and businesses seeking ease with complete functionality.
Also Read: Business Intelligence vs Machine Learning
8.Tablet POS Systems:
Tablet POS systems are contemporary, mobile alternatives in which tablets, commonly iPads or Androids, are used as the primary interface for handling orders and processing transactions, along with enabling various business functions. Lightspeed Restaurant is a full-featured tablet POS system designed for restaurants ranging from fine dining to quick-service.
How It Works:
Tablet POS systems utilize mobile tablets to facilitate order taking, payment processing, and the management of restaurant operations via cloud-based software and wireless connectivity.
Benefits:
1.Simple-to-use interface.
2.Portable with high-functioning capabilities.
3.Less expensive hardware compared to standard systems.
Drawbacks:
1.Tablet limitations in heavy-use cases.
2.Can involve third-party integrations for premium features.
Best for:
Small to medium-size restaurants, cafes, and pop-up concepts.
Also Read: AI for Expanding Restaurant Customer Base
9. Multichannel/Omnichannel POS Systems:
A multichannel POS system allows businesses to accept payments on multiple channels such as online, store, and mobile applications. An omnichannel POS system goes a step further in integrating all these channels to offer a hassle-free customer experience.
Shopify POS is a fine example of an omni channel solution, which integrates in-store and web-based transactions especially for restaurants and is best suited for vendors selling branded goods, meal kits, or merchandise.
How It Works:
Multichannel point-of-sale applications unify sales, inventory, and customer information on physical, web-based, and mobile channels such that business activities flow smoothly and as one unit.
Benefits:
1.Centralized channel order management.
2.Consolidated reporting and inventory tracking.
3.Improved customer experience.
Drawbacks:
1.Can be difficult to implement.
2.May have higher monthly costs.
Best for:
Restaurants with online ordering, third-party delivery, or multiple service channels.
Also Read: What is Ad-Hoc Analysis
How to Choose a POS System for a Restaurant?
Choosing the top restaurant POS system in 2025 is crucial to run your business, boost customer satisfaction and profitability. There are many restaurant POS systems available now- with each system having their own set of features-it is crucial that you identify one that meets your particular needs. Read these step-by-step instructions to help you make the perfect decision:
1. Specify Your Requirements:
Think about your restaurant segment (QSR, full-service, food truck, etc.) and necessary features such as table management, online ordering, or inventory tracking.
2. Select a System Type:
Choose between cloud-based POS (versatile, remote access) or legacy system (local storage, greater control).
3. Designate a Budget:
Include hardware, software subscriptions, and payment processing fees.
4. Prioritize Features:
Seek out primary tools such as sales reporting, CRM, staff management, and third-party integrations.
5. Test Usability:
Ensure that the system is easy to use and train personnel on.
6. Assess Support:
Choose 24/7 customer support and regular training provisions.
7. Plan Ahead:
Ensure the system can grow with your company as it expands.
8. Demo Before You Buy:
Utilize demos or free trials to conduct performance in real-world situations.
Conclusion:
Selecting a proper POS system for restaurants is required in order to maximize the efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall revenue of a restaurant.
The different types of POS systems, i.e., on-premise, cloud, and mobile, possess different strengths appropriate for different business operations.
For example, full-service restaurants can opt for sophisticated systems with table management and kitchen display integration, whereas quick service or fast food restaurants need speed, ease, and mobility.
Cloud POS software is flexible, has real-time data analysis, and remote access and hence ideal for expanding companies or companies with more than one location.
Mobile POS hardware is particularly handy for cafes, food carts, or any business that requires tableside service or quick transaction functionality.
Hybrid systems offer on-premises management supplemented with cloud storage, which restaurants that need security as well as access will value.
Finally, your restaurant’s ultimate POS system will differ based on size, level of service, budget, and long-term goals.
Evaluate your existing needs, long-term objectives, and the support level offered by each vendor.
A properly selected POS system will simplify operations, increase customer satisfaction, and equip you with the analytics to make sound decisions.
Sit down and evaluate your choices and select a solution that addresses the unique needs of your restaurant. If you are still stuck somewhere in selecting the best pos system for your restaurant then feel free to reach us at Livelytics expertise and book a free demo, we are glad to assist you.
