Every business, from tiny coffee roasters to billion-dollar e-commerce businesses, is interested in measuring their success, and determining what works and what doesn’t. This is where Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) come in.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Understanding and using Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is critical for establishing organizational success in today’s data-driven business environment.
KPIs are more than simply spreadsheet figures; they are effective instruments that offer practical insights into a range of corporate domains, including marketing, sales, customer support, and human resources.
Now you might be wondering what is KPI, why it’s important for businesses and how can businesses get an idea of it. Well, if that’s the case, then this blog is all you need.
This blog post will explain what KPIs are, why they are important, how to monitor them, and even provide real-world examples to help you measure and improve your business’s performance.
Also Read: How can Data Analytics Improve the Employee Performance
What are KPIs?
All data points tell a story about your company, but just a handful are critical for determining performance. The key performance indicators (KPIs) that are related to your strategic business goals are the ones you should focus on.
KPIs are Defined as Follows:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are particular measurements that allow businesses to track and measure the efficacy of their actions in accomplishing strategic goals. They are the most important performance indicators for your business at the highest levels of your organization.
Organizations can ascertain whether they are on track to meet their targeted goals by reviewing and assessing KPIs. KPIs provide a concrete means of gauging success, whether it is in monitoring revenue growth, customer satisfaction, or staff productivity.
Analyzing KPIs regularly provides a thorough overview of a business’s performance, allowing those in charge to decide whether to sustain existing activities or develop a new strategy.
All things considered, KPIs assist companies in tracking their progress toward accomplishing their strategic objectives.
Also Read: Benefits of Data-Driven Decision Making
A well-designed KPI strategy measures performance using five to seven criteria. These measures, which offer a targeted and practical way to monitor progress, should be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound).
- Specific: Direction must be clear and detailed. It should provide answers to the following questions: “who,” “what,” “where,” “when,” and “why.”
- Measurable: The KPI should be based on facts that can be precisely measured and tracked.
- Achievable: Given the available resources and time, the KPI ought to be reasonable and reachable.
- Relevant: It must complement the goals of your department or company.
- Time-bound: The KPI should be evaluated within a specified time range, such as weekly, monthly, or quarterly.
6 Best Benefits to Set Up Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
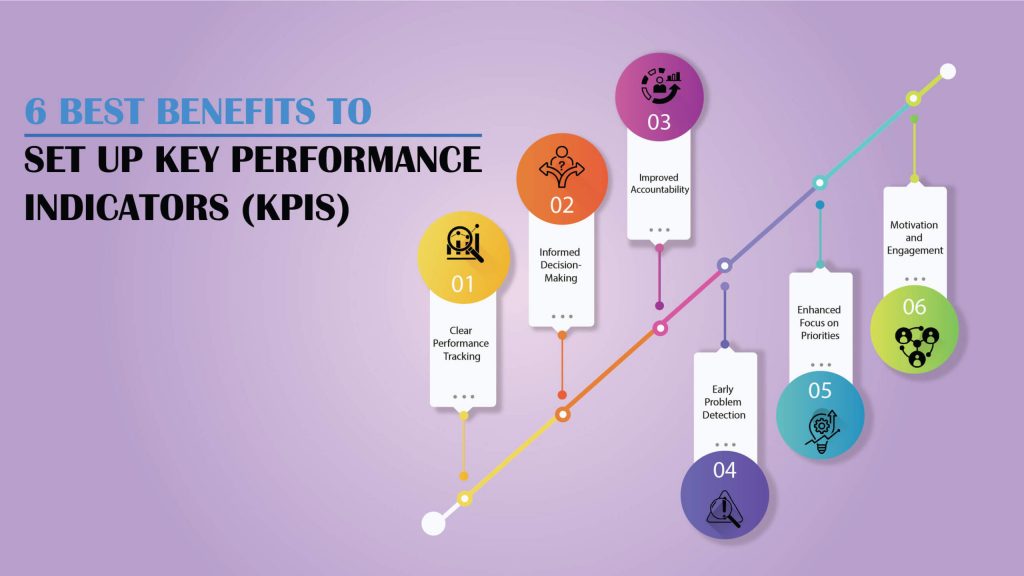
1. Clear Performance Tracking:
KPIs provide clear and comprehensive performance tracking – providing the complete picture of what’s happening around to make decisions that drive business success.
These measurements make assessing progress, making the right decisions, and identifying areas needing attention easier.
Also Read: How AI Unlocks Business Insights that Drive Required Results
2. Informed Decision-Making:
Gone are the days, when decision-makers make decisions based on their gut. Data-driven decisions are taking over and are far more effective than guesswork. KPIs provide the necessary information for making informed choices.
For instance, if a KPI such as customer acquisition cost (CAC) is unusually high, a company can evaluate its marketing and sales strategies to determine where adjustments are needed. This minimizes waste and ensures that resources are allocated efficiently.
Also Read: Improved Decisions through Decision Intelligence
3. Improved Accountability:
Accountability is another factor where key performance indicators help businesses. It establishes clear expectations for teams and individuals by tying performance metrics to specific roles.
For example, a customer service representative might be measured on first response time or first contact resolution.
It makes each department and individual dedicated to their goal, which helps in not only achieving better results but also in fostering a culture of responsibility and ownership across the organization.
Also Read: How to Increase Restaurant Sales Without Advertising
4. Early Problem Detection:
KPIs serve as early warning systems for potential problems. For instance, if the Net Promoter Score (NPS) starts declining, it might indicate customer dissatisfaction.
Early detection through KPI monitoring enables businesses to address issues promptly, preventing minor problems from escalating into major setbacks.
Also Read: Why Does Every Small Business Need Analytics
5. Enhanced Focus on Priorities:
One of the biggest challenges for businesses is staying focused on what matters most. But, KPIs keep everyone hooked to their specific goals and even broader company goals as a whole.
It helps businesses prioritize what matters the most and concentrate efforts on areas with the highest impact. For instance, a company aiming to improve profitability might focus on KPIs like gross profit margin and operating expenses, ensuring these areas receive the necessary attention.
Also Read: The Importance of Customer Analytics In Retail
6. Motivation and Engagement:
When employees can see the results of their efforts through KPIs, it boosts their motivation and engagement.
For example, sales teams tracking lead conversion rates can celebrate incremental progress, which keeps them inspired to aim higher. Additionally, publicizing progress toward team KPIs fosters a sense of shared accomplishment.
Also Read: Leveraging AI to Collect Customer Insights
What are some of the Most Common KPIs that Businesses Track?
Sales KPIs monitor the success of your team’s lead conversion efforts and the efficacy of your sales strategy. Typical sales KPIs consist of:
1. Sales KPIs:
Sales Growth: Calculates the rise in sales over a given time frame.
Customer acquisition cost (CAC): The price of bringing in a new client, which includes sales and marketing expenditures.
Lead Conversion Rate: The proportion of leads that convert to customers.
Value of Sales Pipeline: The entire amount of money that could be made from opportunities in the sales pipeline.
Average Deal Size: The average value of closed sales transactions.
2. Marketing KPIs:
Marketing KPIs assess customer involvement, brand recognition, and campaign efficacy. Typical marketing KPIs consist of:
- Return on Investment in Marketing (ROMI): Measures the revenue gained by marketing initiatives in relation to their expense.
- Lead-to-Customer Ratio: The percentage of marketing leads that convert into actual consumers.
- Website Traffic: The number of people who visit your website.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of persons that responded to an advertisement or marketing message.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): The estimated revenue that a company can expect from a customer during their lifetime.
Also Read: How to Use AI in the Restaurant Business
3. Customer Service KPIs:
Customer service KPIs monitor the effectiveness of your staff in assisting clients and addressing problems. Typical KPIs for customer service include:
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): A metric for determining customer satisfaction with a product or service.
- First Response Time: The typical amount of time it takes for a customer support agent to reply to a query from a client.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measures client loyalty by asking customers how likely they are to refer your business to others.
- First Contact Resolution (FCR): The percentage of customer issues handled during the first interaction.
- Customer Retention Rate: The proportion of clients who stick with a business over a given time frame.
Also Read: How AI Revolutionizes Customer Experience in the Restaurant Industry
4. Human Resources & Employee Turnover KPIs:
Human resource KPIs assess the efficacy of personnel management, recruiting, and retention. Common human resource KPIs include:
- Employee Turnover Rate: The percentage of employees who depart the organization within a given timeframe.
- Time to Fill: The typical amount of time needed to fill a vacancy.
- Employee engagement: Employee engagement is a measure of how emotionally committed employees are in their jobs.
- Training ROI: Examines the advantages of staff training, such as increased productivity or decreased attrition, and weighs them against the expense.
- Diversity Rate: Measures how inclusive your workforce is in terms of age, gender, and color.
5. Financial Performance KPIs:
Financial performance KPIs track a company’s ability to generate profits and maintain financial stability. Key examples include:
- Gross Profit Margin: Indicates the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS), reflecting profitability from core operations.
- Net Profit Margin: Measures how much of the revenue translates into actual profit, highlighting overall financial efficiency.
- Operating Expense Ratio (OER): Compares operating expenses to total revenue, helping evaluate cost management.
- Current Ratio: A liquidity measure that shows the company’s ability to cover short-term liabilities with current assets.
- Revenue Growth Rate: Tracks the percentage increase in revenue over a given period, signifying business expansion.
6. Operational Efficiency KPIs:
Operational efficiency KPIs assess how effectively resources are utilized to achieve desired outcomes. Common examples include:
- Order Fulfillment Cycle Time: Monitors the time it takes to complete an order, from receipt to delivery, reflecting process efficiency.
- Inventory Turnover: Tracks how often inventory is sold and replaced over a specific timeframe, ensuring effective stock management.
- Production Efficiency Rate: Measures output relative to input, helping identify areas for process optimization.
- Downtime Rate: Evaluate the percentage of time operations are idle or interrupted, impacting productivity.
- Cost Per Unit: Determines the average cost to produce or deliver a single product or service, supporting pricing and cost-control strategies.
Common Mistakes While Using KPIs and How to Avoid Them

KPIs can be immensely helpful when used properly, but some typical mistakes might reduce their efficacy. Continue reading to learn more about the common issues that businesses experience when setting up KPIs and how to address them effectively.
1. Focusing mainly On the Vanity Metric:
Businesses that place too much emphasis on vanity metrics—numbers that might appear impressive on paper but don’t have a big impact on project success—may make poor choices.
However, it’s critical to focus on KPIs that are directly related to the strategic goals and outcomes of your project. Therefore, be sure to concentrate on indicators that enhance your company’s value.
2. Overlooking Qualitative Indicators:
Another typical mistake is to ignore qualitative indicators. While qualitative KPIs offer less concrete but equally valuable information, such as team happiness, customer feedback, or the perceived quality of project outputs, quantitative KPIs offer a clear, quantifiable evaluation of specific project components.
Therefore, don’t forget to overlook it. If you’re unsure how to track qualitative KPIs, the greatest data platform is all you need.
3. Lack of Documentation:
Furthermore, a lack of documentation could lead to chaos. Even if you are capturing everything, failing to document will result in the same issues down the road. Keep track of your progress and have each KPI documented, regardless of whether you reach or fall short of your goals.
These insights can help you grow and get better for subsequent initiatives. When you have the best AI data tool on your side, though, this is not an issue. It automatically records everything, allowing you to check out anytime, place.
Also Read: Choosing the Right AI Data Platform for your Business
4. Keeping to the Same KPIs:
As the market evolves, your firm expands, consumer tastes shift, and other things change, keeping to the same KPIs will limit your growth. By periodically evaluating and modifying your KPIs, you can make sure they stay applicable and useful for the duration of the project.
5. Ignoring KPI Alignment with Business Goals:
One of the biggest mistakes businesses make is setting KPIs that do not align with their overall strategic objectives. If your KPIs are disconnected from your company’s mission and goals, they can lead to wasted resources and misleading insights. So, ensure that your KPIs support broader business goals and contribute to measurable success.
6. Failure to Act on KPI Insights:
Collecting KPI data without taking action is another common pitfall. Even the most well-defined KPIs are useless if they don’t drive informed decision-making.
Businesses must establish clear action plans based on KPI results and use insights to refine strategies, optimize performance, and address inefficiencies.
Having an AI-powered data platform can simplify this process by providing real-time recommendations and automating necessary adjustments.
How to Establish KPIs?
Setting KPIs in project management is an art that involves a combination of strategic vision, a thorough understanding of project objectives, and an intuitive sense of what matters to measure.
Here are six actions you can take to determine the appropriate key performance indicators for your projects and specific business operations.
Step 1: Recognize the Project’s Goals:
The first step includes a detailed understanding of project objectives. What goals do you hope to accomplish with this project? What would you like to measure? Where do you want key performance indicators to lead you?
These objectives should represent your business’s unique goals and what you hope to accomplish in a given amount of time.
Step 2: Connect Your Goals to Your KPIs:
Once you’ve established your goals, you can begin to determine the metrics that will track your progress toward them. Each KPI should be linked to a particular project goal in order to track performance and progress toward those goals.
Make a list of all the possible measurements that fit each target area. Consider using both quantitative and qualitative indicators to gain insight into the specific component of performance you wish to track.
Divide each business goal into distinct components or major focal areas. For example, if your goal is to improve customer satisfaction, relevant emphasis areas could be response time, complaint resolution rate, or client retention.
Step 3: Describe What Success is:
What is the best way to know that you are headed in the right direction toward your goal? In order to get this knowledge, you must first decide what success means for the goals you have already established.
Put simply, you must incorporate important, quantifiable outcomes into your business goal.
Now let’s return to the example from Step #2: If you want to improve customer experience, success could be defined as achieving a 20% increase in Net Promoter Score (NPS), reducing average response times to under 24 hours, or attaining a 95% customer satisfaction rate within six months.
Consider using a mix of short-term and long-term indicators. Short-term indicators can include metrics like the number of resolved complaints in a given week, while long-term indicators might focus on sustained client retention rates over a year. Both perspectives provide a comprehensive view of your progress.
Step 4: Establish a Method for Measuring KPIs:
Once you’ve set your business’s KPIs, it is important to determine how you’ll measure and track them. Establishing a reliable measurement system ensures consistency and accuracy in your performance evaluation.
Start by identifying the tools and systems you need, such as project management software, analytics platforms, or CRM systems that can automate data collection. Define a clear process for gathering, analyzing, and reporting KPI data regularly.
It’s also important to assign responsibilities to specific team members who will be accountable for tracking and reporting KPIs.
Regular check-ins and progress updates should be scheduled to review KPI performance and make necessary adjustments to stay on track. Ensure that your measurement methods are aligned with your business operations and can provide real-time insights when needed.
Step 5: Review and Refine KPIs Regularly:
KPIs should not be set in stone; they need to evolve as your project progresses and business needs change. Regularly reviewing and refining your KPIs helps ensure they remain relevant and aligned with your overarching goals.
Schedule periodic KPI reviews—whether monthly, quarterly, or at key project milestones—to analyze whether the metrics are effectively measuring performance and driving desired outcomes. During these reviews, assess if any adjustments are needed, such as redefining targets, modifying data sources, or adding new KPIs to reflect shifting priorities better.
Engage stakeholders, team members, and leadership in the review process to gain diverse perspectives on KPI effectiveness and potential improvements. Being flexible and adaptable in your approach ensures long-term success and continuous growth.
Also Read: Data-Driven Social Media Strategies for Your Business
Step 6: Leverage Insights to Make Data-Driven Decisions:
The final step in establishing KPIs is using the collected data to make informed, strategic decisions. With well-defined KPIs in place, businesses can identify trends, pinpoint areas for improvement, and capitalize on opportunities for growth.
Leverage data visualization tools and dashboards to easily interpret KPI trends and compare them against established benchmarks. Use these insights to make proactive adjustments, optimize processes, and allocate resources effectively.
Furthermore, communicate KPI insights across the organization to ensure transparency and alignment with business objectives. When everyone understands performance metrics and their impact, it fosters a culture of accountability and continuous improvement.
By following these steps, businesses can establish meaningful KPIs that drive success, improve project outcomes, and align with long-term strategic goals.
To Wrap Up!
KPI tracking is essential to the success of your company. However, it doesn’t have to be a difficult task. Choosing the correct KPIs and using tools to track them can help you make educated decisions to expand your business.
And if you want to do it effortlessly, Livelytics has you covered. It is a one-of-a-kind AI platform that will help you embrace the power of KPIs while unlocking the potential for growth and continual improvement.
Livelytics helps businesses take full control of their KPIs with its powerful data analytics, sophisticated tools, and out-of-the-box features. It simplifies the entire KPI process—from creation to ongoing optimization—by providing actionable insights that drive better decision-making.
Overall, Livelytics empowers businesses to not only track their progress but to continuously refine and optimize their KPIs, ensuring long-term success and data-driven growth. To check out more about Livelytics, book a free demo now.
