Introduction
Machine learning (ML) and business intelligence (BI) are potent data-driven technologies revolutionizing how companies operate and make decisions. These two are growing at an unprecedented pace and show no signs of stopping down.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!The machine learning industry is expected to grow at an incredible 36.08% annual growth rate (CAGR 2024-2030) to reach US$79.29 billion by 2024. On the other hand, the worldwide business intelligence market is predicted to rise from $29.42 billion in 2023 to $54.27 billion in 2030.
When combined together, it can transform how businesses operate and can take their growth to new heights of success. However, to make the most out of these technologies – it is important to understand their basics, similarities, and differences.
This article delves into the fundamental differences between business intelligence and machine learning in terms of goals, techniques, outputs, data requirements, use cases, users, and supporting technologies.
Let’s get going!
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence and it is an approach that learns from experience and becomes more intelligent rather than relying solely on algorithms or scripts. Machine learning algorithms are built to learn from experience, in contrast to traditional software that depends on explicit programming.
They achieve this through the analysis of enormous volumes of data, the discovery of hidden patterns, and even the formulation of data-driven future predictions.
Machine-learning algorithms have transformed several industries, including healthcare, banking, retail, and manufacturing, by automating processes, maximizing efficient resource allocation, and revealing actionable insights from data.
As the volume and complexity of information increases, the demand for ML expertise and programs is expected to rise, fueling innovation and transformation across various fields.
Also Read: How do Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Helps Businesses
How Does it Help Businesses?
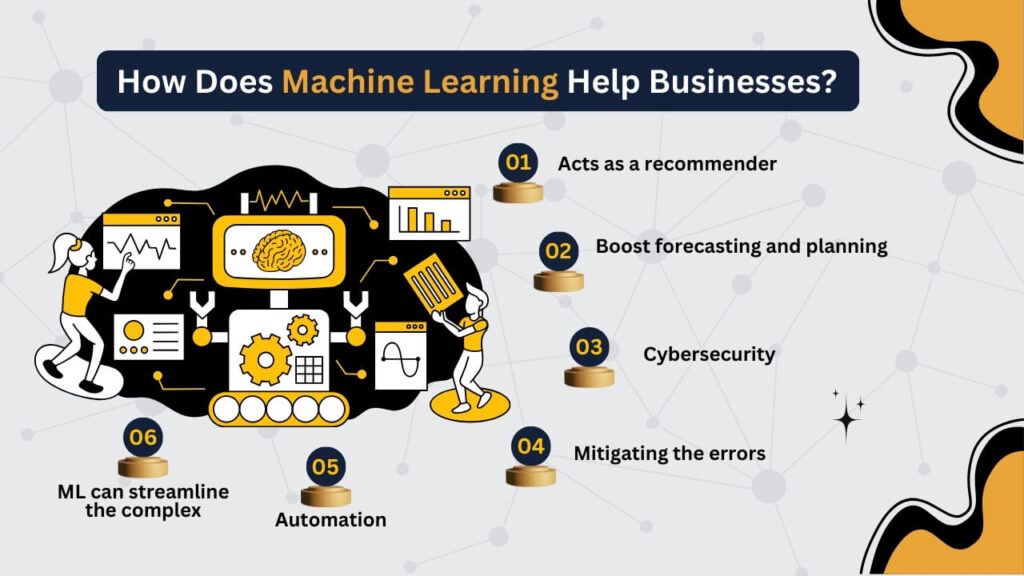
- Acts as a recommender: Netflix and Amazon are well-known examples of companies utilizing machine learning to create recommender systems that recommend new products or services according to a customer’s purchasing history. This ML use case increases value for consumers and gives businesses the chance to upsell and cross-sell, which generates additional revenue streams.
- Boost forecasting and planning: As machine learning is all about forecasting, the technology provides a natural foundation for planning and forecasting tasks. Businesses may better plan their budgets and safeguard their financial futures by using machine learning (ML) to forecast future costs, demand, and price trends.
- Cybersecurity: It is another area where machine learning is having a significant impact. Machine learning eliminates the need for ongoing human observation by identifying trends, resolving inaccurate data, methodologies, and discrepancies in data, and instantly adjusting to new threats. This frees up enterprises to concentrate on other crucial areas.
- Mitigating the errors: The machine just understands precision. Once given proper instructions, the computer exactly executes them, providing only accurate and dependable data to the end consumers. It means that “human factor” errors may disappear from your automated operations. A proper machine learning algorithm will relieve your employees of repetitive and tedious activities.
- Automation: ML deployment can be beneficial in automation, which improves several company processes, including communications, marketing, onboarding, and support. Automated procedures give you the flexibility to focus on more imaginative and challenging projects in place of the repetitive, small-task routine.
- ML can streamline the complex: Machine learning helps businesses handle complex tasks more efficiently. By analyzing vast amounts of data, it identifies patterns and trends that might be too difficult for humans to catch. For example, it can streamline predicting customer preferences, optimizing inventory levels, or even detecting fraud. Instead of manually sorting through endless information, businesses can rely on machine learning to make smarter decisions faster, leading to better outcomes and improved productivity.
Also Read: Advantages of Business Intelligence in Retail Industry
What is Business Intelligence?
Business intelligence is a technology-driven process that collects data from a range of sources, including external resources like social media, reviews of market studies, and enterprise databases, as well as internal structures like databases, CRM structures, ERP structures, and organization resource-making plans (ERP) structures.
The system cleans, processes, and converts the combined data into useful formats such as dashboards, reports, and visualizations. Imagine having a crystal-clear view of your company’s performance, exposing trends, patterns, and important data at a glance.
While traditional business intelligence (BI) mostly relies on IT specialists, modern BI empowers business users to generate their own information independently. At its core, BI strives to answer crucial questions, discover hidden patterns, tendencies, and correlations in data, and offer stakeholders valuable statistics to drive business growth and innovation.
How Does it Help Businesses?
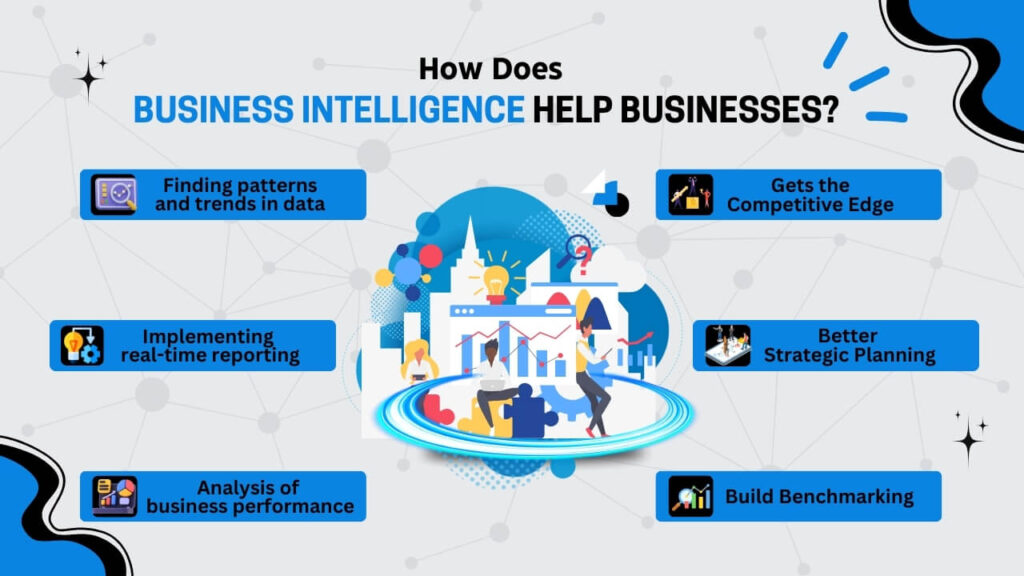
- Finding patterns and trends in data: BI makes it easier to spot patterns and trends in corporate data. This can lead to better-informed decisions. It can identify trends and help with decision-making by examining sales, customer, or operational variables over an extended period of time.
- Implementing real-time reporting: BI enables real-time reporting of company metrics. It is possible for businesses to continuously track the key performance metrics. This makes it easier for companies to react swiftly to shifting market dynamics or operational problems.
- Analysis of business performance: BI allows you to assess previous business performance across a wide range of variables, including revenues, costs, client retention, and more. Businesses can learn what is working and where they might be able to improve by identifying bottlenecks and underperforming areas.
- Gets the Competitive Edge: Businesses can gain a competitive edge by tracking market trends and competitors to spot new business possibilities with the use of BI-driven insight. Additionally, it can enhance the pace of decision-making and enable businesses to beat competitors to market with faster time-to-market.
- Better Strategic Planning: For better strategic planning, employees need to spend all day or all week gathering data and making a sense of it. However, BI automates labor-intensive and time-consuming tasks, freeing up staff members to concentrate on utilizing the data, making decisions, and acting on it. To put it simply, by doing the things that add value and automating the repetitive.
- Build Benchmarking: Companies that implement Business Intelligence can index their data, set benchmarks, and track their progress on a continuous basis. These help organizations to make choices swiftly, operate more effectively, have happier clients, experience higher customer retention rates, and frequently increase sales.
Also Read : How Business Intelligence is Helping Business?
Business Intelligence vs Machine Learning: The Major Differences!
BI and ML are two popular technologies that businesses are leveraging to streamline a lot of their tasks & processes. These are trendy, widely used, and offer much-needed insights, with several similarities in how they help businesses make data-driven decisions. Although, apart from similarities – there are some differences which make them stand out. Let’s find out the differences:
Here’s a more detailed table explaining the differences between Machine Learning (ML) and Business Intelligence (BI):
| Aspect | Business Intelligence (BI) | Machine Learning (ML) |
| Primary Function | BI focuses on analyzing historical data to generate insights, dashboards, and reports. It helps businesses understand past performance and make informed decisions based on that data. | ML goes beyond historical analysis by using algorithms to learn from data patterns and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. |
| Focus | BI centers on descriptive and diagnostic analytics, helping businesses understand what happened and why it happened in the past. It is primarily used for performance tracking, monitoring KPIs, and identifying trends based on historical data. | ML focuses on predictive and prescriptive analytics, aiming to forecast what will happen in the future and suggesting what actions should be taken to optimize outcomes. It goes beyond pattern identification to actively predict and adapt. |
| Data Usage | BI works mostly with structured data, such as financial records, sales data, and operational metrics, which are organized in a clear format. It tends to analyze large volumes of historical data but it’s not quite helpful in processing unstructured or complex datasets. | ML can handle both structured and unstructured data (e.g., text, images, audio). It can use historical data, real-time data, or a mix of both. ML models can also process complex datasets like social media feeds, customer reviews, and multimedia data to make predictions. |
| Human Involvement | BI requires significant human involvement. Business analysts and decision-makers must interpret the data and insights provided by BI tools to make decisions. It’s a human-guided process where professionals explore the data and draw conclusions. | ML is more autonomous. Once the models are trained, they can continue to learn from new data, make predictions, and recommend actions with little human intervention. It requires less ongoing human oversight, though data scientists and engineers need to build and fine-tune the models. |
| Complexity | BI systems are relatively straightforward to implement and use, especially when companies already have clean, structured data. The focus is on user-friendly tools that enable business users to generate insights with minimal technical expertise. | ML is more complex to implement and maintain. It requires a deep understanding of data science, machine learning algorithms, and programming languages. However, you can simply leverage the tool with ML capabilities for easy implementation. |
| User Base | BI is typically used by business analysts, managers, executives, and decision-makers who need to understand business performance and make strategic decisions based on past trends. It is accessible to non-technical users through intuitive dashboards and visual reports. | ML is mainly used by data scientists, machine learning engineers, software developers, and sometimes tech-savvy business professionals. These users build, train, and refine models to predict future business outcomes and improve operations. |
| Adaptability | BI systems are not adaptive on their own. They require manual updates and adjustments as new data is introduced. Business analysts or IT teams need to update the system or change the data models to reflect new insights or data trends. | ML systems are adaptive and can continuously learn from new data without needing constant manual updates. As more data flows in, ML models refine their predictions and improve their accuracy over time, making them highly dynamic and self-improving. |
| Use Case Examples | BI is commonly used for sales reporting, performance monitoring, financial analysis, and operational efficiency tracking. For example, a retailer might use BI to understand which products performed best over the last quarter and identify patterns in customer behavior. | ML is used in more advanced applications such as fraud detection, recommendation engines, predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, and customer segmentation. An online store, for instance, might use ML to predict which products customers are likely to purchase next based on browsing behavior. |
| Cost & Resources | BI systems are generally less costly to implement and maintain compared to ML systems, especially for companies that already have structured data in place. BI systems are designed for widespread use across many departments. | ML can be more costly to develop and implement, requiring significant investments in developing technical infrastructure. However, ML offers higher long-term value for businesses. Although, there are cost-effective AI tools with ML capabilities to make the most out of data and this powerful technology. |
| Scalability | BI can be scaled across multiple departments for analyzing different types of structured data, but it may struggle with scaling if a company starts working with complex, unstructured data or requires real-time processing. | ML is highly scalable, especially when dealing with large and complex datasets across various departments. It can handle growing data streams and scale easily to accommodate increasing amounts of data. |
Also Read: Artificial Intelligence Vs Machine Learning
So, which one to choose?
So, here we are after the complete wrap-up – right from clearing the basics, discussing its advantages, and also how these two technologies differ from each other – it’s now the time to decide which one to choose. Are you more into BI or shifting towards ML?
But, in the end, it all boils down to what your business needs and what are your goals.
Here’s the best part: there is no need to choose. For many businesses, the best approach is to integrate both BI and ML. BI gives you clarity on what’s happened, while ML helps predict what’s next, creating a balanced data strategy that’s both reactive and proactive.
If you are looking forward and are confused about how to get started, Livelytics has got you covered. It is the best-in-class AI data platform with ML and BI capabilities, that is curated for the hospitality, restaurant, salon, retail, insurance, and finance industries. If you want, we can even help you create a custom platform for you.
So, what are waiting for? Book a free demo now and see why it’s the best for your business.
What’s the Key takeaway?
Machine learning (ML) and business intelligence (BI) are both important tools for translating data into meaningful insights. BI excels at interpreting historical context, while ML is best at uncovering hidden patterns and forecasting the future.
So, BI and ML are not competitors. They are complementary forces.
Businesses can obtain a full picture of their operations, customers, and market trends by combining the predictive power of machine learning (ML) with the clear data visualization of business intelligence (BI). They can remain ahead of the curve, maximize performance, and make wiser judgments with this.
As you explore the potential of machine learning and business intelligence to improve your business, keep in mind that Livelytics is here to help. It is a powerful, feature-rich AI data platform with BI and ML capabilities helping businesses to make the most of their data and take their business to new heights of success.
To know more about how Livelytics can help you, book a free consultation and get started right away!